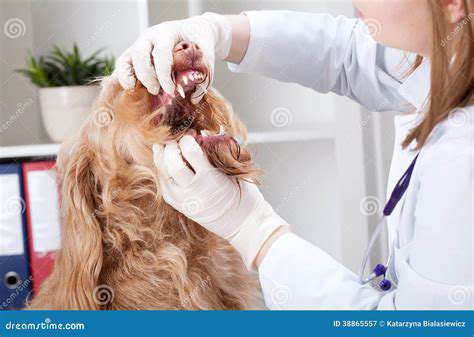
Recognizing the Signs of Dental Disease in Pets
Visual Clues: Examining Your Pet's Mouth
Understanding Body Language
Observing your pet's body language is crucial for recognizing subtle signs of discomfort, illness, or stress. A drooping tail, tucked ears, and a flattened posture can all indicate fear or anxiety. Understanding these subtle cues can help you identify problems early and provide appropriate support. It's important to pay attention to the context of these behaviors. For example, a dog normally friendly might exhibit these signs when faced with a new and overwhelming environment.
Different breeds and individual pets may have unique ways of expressing themselves, so it's essential to familiarize yourself with your pet's normal behavior. This allows you to quickly identify any deviations and address any potential concerns.
Ear Position and Movement
The positioning of your pet's ears can offer significant clues about their emotional state. Ears held high and forward often indicate alertness or interest, while flattened ears can signify fear or aggression. Observe how your pet's ears move in response to different situations. Are they twitching, swiveling, or remaining still? These subtle movements can provide valuable insights into their current emotional state.
Eye Contact and Gaze
Eye contact is another important aspect of body language. A direct gaze can signal confidence and alertness in some animals. However, excessively staring or dilated pupils might indicate stress or anxiety. Likewise, avoidance of eye contact can also be a sign of discomfort or fear. Remember to consider the overall context of the interaction and your pet's usual behavior.
Tail Wagging and Movement
Tail wagging is often associated with happiness and excitement, but the speed, intensity, and direction of the wag can vary significantly. A slow, subtle wag can sometimes indicate nervousness or uncertainty, while a rapid, high-energy wag often signifies strong enthusiasm. Pay attention to the context of the wagging. A dog might wag its tail excitedly when playing with a toy, but nervously when encountering a stranger.
Facial Expressions
Facial expressions, though sometimes subtle, can be highly informative. A relaxed, open mouth with visible teeth might signal contentment, while a tense or snarling expression could suggest aggression or discomfort. A lowered muzzle, tucked lips, or a wrinkled forehead could be indicative of pain or stress. It's important to consider the overall body language, including the position of the ears, eyes, and tail.
Vocalizations
Vocalizations, such as meows, barks, or growls, are crucial communication tools for pets. Understanding the specific types of vocalizations can provide valuable insights into their emotional state. A high-pitched whine may indicate distress, while a low growl might suggest a warning. The tone, volume, and duration of vocalizations can all offer valuable information about your pet's feelings.
Environmental Cues
The environment itself can play a significant role in interpreting your pet's body language. A change in behavior, such as hiding or avoiding certain areas, could indicate a problem with the environment. A pet might be exhibiting unusual behaviors in response to a new smell, noise, or person in their surroundings. Paying attention to these environmental cues, along with body language, can help you address any concerns promptly.