Understanding Pet Heartworm Disease: Prevention and Treatment
Understanding Heartworm Disease
Heartworm disease, a serious and potentially fatal condition, is a parasitic infection affecting dogs and other canine species. Caused by parasitic worms called heartworms, this disease primarily affects the heart and lungs, though other organs can be impacted. Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial to preventing significant health complications and ensuring a positive outcome for your pet.
These microscopic worms are transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito. While seemingly innocuous, the infection can progress insidiously, leading to severe and often irreversible damage over time. Therefore, understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and preventive measures is paramount to pet ownership.
Recognizing the Early Symptoms
Early detection is key to successful treatment. Unfortunately, heartworm disease often progresses without noticeable symptoms in the initial stages. However, some subtle signs can appear early, including a slight cough, lethargy, or a reduced appetite. These symptoms may be easily overlooked, particularly if they are mild or intermittent.
It's important to note that these early signs can be mistaken for other conditions. Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial for early detection and diagnosis, as subtle changes in your pet's health can be indicative of a larger problem.
Progression to More Severe Symptoms
As the infection progresses, more pronounced symptoms may develop. These can include persistent coughing, difficulty breathing, weight loss, swelling in the abdomen, and a distended chest cavity. These symptoms are often more obvious and cannot be ignored.
In advanced cases, heartworm disease can cause severe damage to the heart and lungs, leading to congestive heart failure. This is a critical condition that requires immediate veterinary intervention.
Complications from Heartworm Disease
The complications of heartworm disease can be severe and life-threatening. Damage to the heart can lead to heart failure, causing fluid buildup in the lungs and other parts of the body. Additionally, heartworm disease can cause damage to the lungs, leading to respiratory distress and difficulty breathing.
Furthermore, the presence of adult heartworms can cause blockages in blood vessels throughout the body. These blockages can lead to organ damage and even death. The severity of these complications often depends on the duration and extent of the infection.
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosis of heartworm disease typically involves a combination of physical examination, blood tests, and possibly imaging techniques such as X-rays or echocardiograms. These tests help to visualize the presence of heartworms in the heart and blood vessels, and assess the overall condition of the cardiovascular system.
Veterinary professionals use specific blood tests to detect heartworm antigens or antibodies. These tests are crucial for confirming the presence and extent of the infection, enabling prompt and effective treatment strategies.
Treatment Options for Heartworm Disease
Treatment for heartworm disease varies depending on the stage of infection and the overall health of the pet. It is imperative to follow the veterinarian's instructions carefully during and after treatment. Some treatment protocols involve administering medication to kill the adult heartworms while others involve more extensive procedures.
Treatment often involves a multi-part process that must be carried out over several weeks, or even months, under the strict supervision of your veterinarian. The treatment process is designed to eliminate the adult heartworms and prevent further complications.
Prevention and Vaccination
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to potentially life-threatening conditions like heartworm disease. Regular preventative medication, administered by your veterinarian, can effectively prevent heartworm infection. These medications should be given monthly to effectively stop the life cycle of the disease in your pet.
Vaccinations are not available to prevent heartworm disease, as it is caused by parasites, not viruses. However, regular veterinary care and preventative medication can significantly reduce your pet's risk of contracting this serious illness.
When choosing citrus fruits, look for those that are firm to the touch. Avoid any that feel soft, mushy, or have noticeable blemishes. The skin should be smooth and free of any significant damage or bruising. A bright, vibrant color is generally a good indicator of ripeness and freshness. Consider the specific type of citrus fruit you're purchasing – oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruits, mandarins – as each might have slightly different visual characteristics when ripe and ready to eat. Paying close attention to these details will help you select the most flavorful and enjoyable citrus fruits.
Treatment Options for Heartworm Disease: Considerations and Challenges
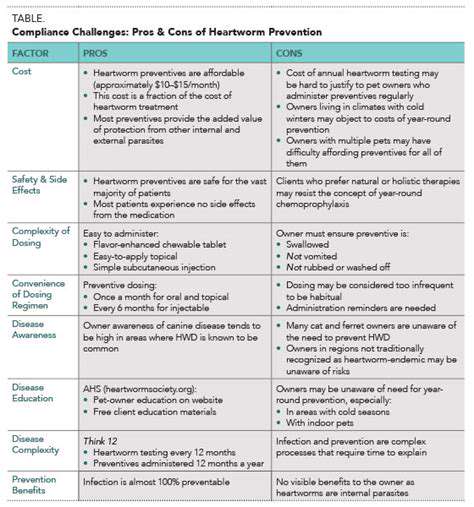
Medication Therapy
Medication, often the first line of treatment for heartworm disease, involves a series of potent antiparasitic drugs. These drugs target the adult heartworms, aiming to eliminate them from the circulatory system. The medication regimen often requires several weeks of administration, and close veterinary supervision is crucial to ensure its effectiveness and to monitor for any adverse reactions. This treatment is generally effective for early-stage infections, but more advanced cases might require more aggressive or combined treatments.
Surgical Intervention
Surgical removal of adult heartworms is a viable option in certain cases, especially when the infection is localized or involves a smaller number of worms. This procedure involves carefully extracting the heartworms from the affected areas, typically the heart or pulmonary vessels. However, surgical intervention is often more complex and carries a higher risk compared to medication therapy, especially in cases with extensive or diffuse infection.
Supportive Care
Supportive care plays a vital role in managing the symptoms and complications associated with heartworm disease. Veterinary intervention may involve administering fluids to maintain hydration and electrolytes, as well as medications to address specific symptoms like coughing or shortness of breath. Careful monitoring and supportive care can significantly improve the comfort and well-being of the pet during the treatment process. This aspect of treatment is particularly important for managing the secondary effects of the infection and improving the overall prognosis.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are crucial for both preventing and managing heartworm disease. Restricting a pet's activity levels during the acute phase of infection can help reduce strain on the cardiovascular system. This is often recommended, especially for more severe cases. This approach helps to ensure the body's resources are focused on recovery rather than strenuous exertion that could exacerbate the condition. Providing a comfortable and supportive environment is equally important.
Diagnostic Testing
Effective treatment hinges on accurate diagnosis. Veterinary professionals utilize various tests to detect the presence and extent of heartworm infection. These tests, such as blood tests and imaging techniques, help determine the appropriate course of treatment. Early and accurate diagnosis is paramount for successful management and to prevent the progression of the disease to more critical stages. This ensures that the treatment plan is tailored to the specific needs of the infected animal.
Monitoring and Follow-up Care
Regular monitoring and follow-up care are essential components of treatment. This includes periodic blood tests and physical examinations to assess the response to treatment and monitor for any recurrence or complications. Veterinarians closely track the reduction in worm burden and the overall health of the animal. This ongoing monitoring ensures that the treatment is effective and that any emerging issues are addressed promptly.
Complementary Therapies
While not a primary treatment modality, complementary therapies can support the overall well-being of the pet during heartworm treatment. These therapies might include nutritional supplements to boost the immune system or stress-reducing measures to promote recovery. These measures are often used in conjunction with conventional treatments. They can play a supportive role in managing symptoms and promoting overall health. However, it's crucial to discuss any complementary therapies with the veterinarian before implementation to ensure they don't interfere with the primary treatment protocol.
