How to Administer Subcutaneous Fluids to Your Pet
Choosing the Right Subcutaneous Site and Technique
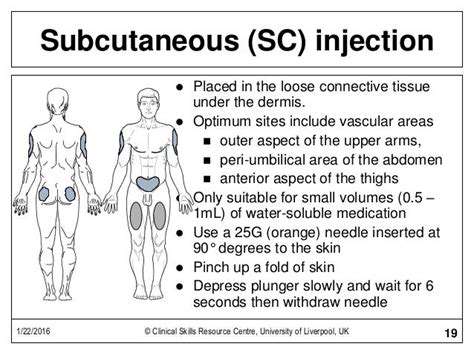
Key Considerations for Subcutaneous Implant Selection
When deciding on a subcutaneous implant, multiple critical aspects demand attention. The perfect match depends on balancing medical requirements with individual patient factors. Every person's anatomy and health profile differ, making personalized assessment non-negotiable for successful outcomes.
Material selection goes beyond basic compatibility. The ideal substance should integrate seamlessly with bodily tissues while maintaining structural integrity for years. Recent advancements in biomaterials have expanded options, but thorough testing remains essential. Always verify long-term clinical performance data before committing to specific materials.
Optimizing Implant Dimensions
Size matters tremendously in subcutaneous applications. An improperly sized implant can cause everything from minor irritation to complete functional failure. Precision measurement tools and 3D modeling now allow for custom-fitted solutions in complex cases. The days of one-size-fits-all approaches are ending as personalized medicine advances.
Shape considerations involve more than aesthetics. The contour must complement natural body mechanics while fulfilling its intended purpose. Ergonomic design principles should guide every implant's development, ensuring comfortable long-term wear without compromising performance.
Modern manufacturing techniques enable previously impossible geometries. Laser scanning and additive manufacturing can produce implants matching patient anatomy with 0.1mm precision. This technological leap has dramatically reduced adjustment periods and improved patient satisfaction rates.
Durability factors deserve equal attention. The implant must withstand years of mechanical stress without degradation. Material scientists now incorporate nanotechnology to enhance strength while reducing weight, creating solutions that feel increasingly natural over time.
Proper sizing affects more than comfort. Research shows correctly dimensioned implants integrate better with surrounding tissues, reducing rejection risks and improving functional outcomes. This makes the measurement phase arguably the most critical step in the process.
Recognizing and Responding to Potential Complications

Understanding Procedure Risks
All medical interventions carry inherent risks that responsible patients should understand. Informed consent requires transparent discussion of possible adverse outcomes, from temporary discomfort to rare but serious events. Modern risk assessment tools can now predict complication likelihood with surprising accuracy.
Complication severity often relates to early detection. New monitoring technologies enable real-time tracking of implant integration, allowing immediate intervention when needed. Patients should receive clear guidelines about warning signs requiring prompt medical attention.
Post-Procedure Management Strategies
Recovery protocols have evolved significantly in recent years. Evidence-based rehabilitation programs now shorten recovery times while improving outcomes. The old wait and see approach has been replaced with active recovery strategies backed by clinical research.
Follow-up care makes the difference between good and excellent results. Smart implants with embedded sensors now provide continuous performance data, alerting clinicians to potential issues before symptoms appear. This proactive approach has revolutionized postoperative monitoring.
Mitigating Individual Risk Factors
Personalized risk assessment has become standard practice. Genetic testing can now identify predisposition to certain complications, allowing for customized prevention strategies. This represents a major shift from reactive to preventive medicine.
Lifestyle modifications significantly impact recovery trajectories. Nutritional optimization and targeted exercise programs have shown remarkable results in reducing complication rates across all patient demographics. The most successful outcomes often involve multidisciplinary care teams.
Chronic condition management deserves special attention. Integrated care models that coordinate treatment for comorbidities produce superior results compared to isolated interventions. This holistic approach represents the future of complication prevention.